We tend to think of wolves as apex predators, feared by many and respected by all. However, these powerful canines aren’t invincible. In the wild, wolves face threats from various organisms, ranging from tiny parasites to large carnivores. I was quite surprised when researching this piece just how many other organisms prey on wolves.
Grizzly Bears
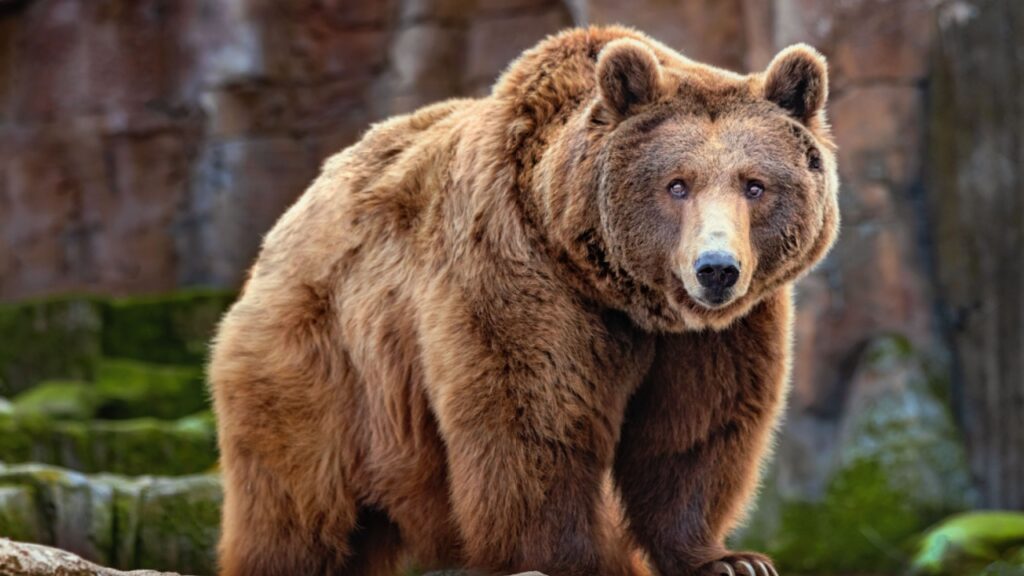

Grizzly bears are one of the few animals that can overpower an adult wolf. These massive omnivores occasionally prey on wolves, especially if food is scarce. In areas where grizzlies and wolves coexist, bears have been known to steal wolf kills and even attack wolf dens.
Mountain Lions
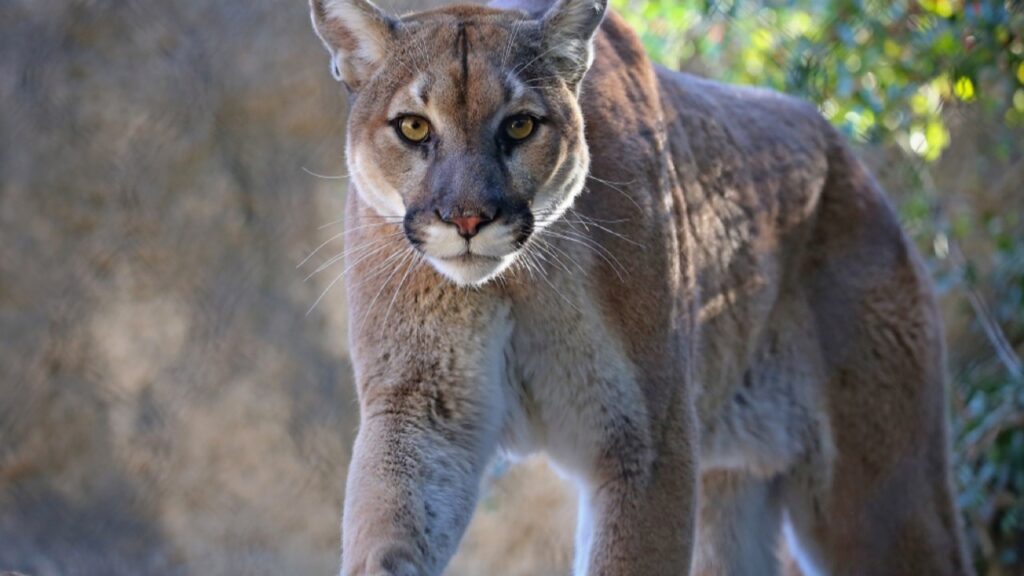

Also known as cougars or pumas, mountain lions are skilled predators that sometimes target wolves. They’re especially dangerous to lone wolves or pups. Mountain lions use their stealth and powerful build to ambush wolves, often attacking from above.
Tigers
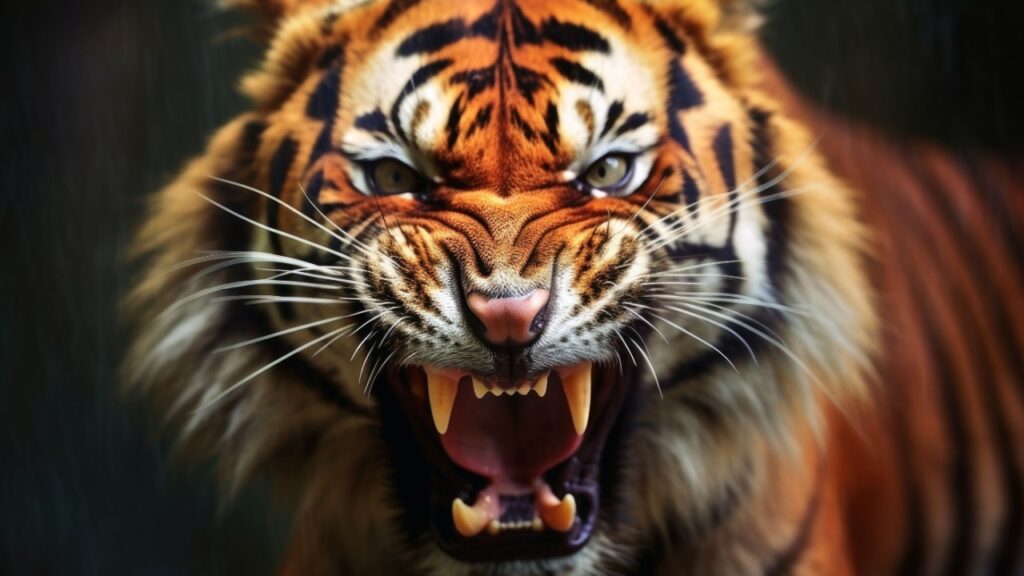

In parts of Asia where wolves and tigers share habitats, tigers can be formidable predators of wolves. Siberian tigers, in particular, have been observed hunting and eating wolves. The sheer size and strength of tigers make them a serious threat to wolf packs.
Humans

Historically, humans have been one of the biggest threats to wolf populations. Through hunting, trapping, and habitat destruction, humans have dramatically reduced wolf numbers in many areas. Even today, human activities continue to impact wolf populations worldwide.
Parasitic Worms
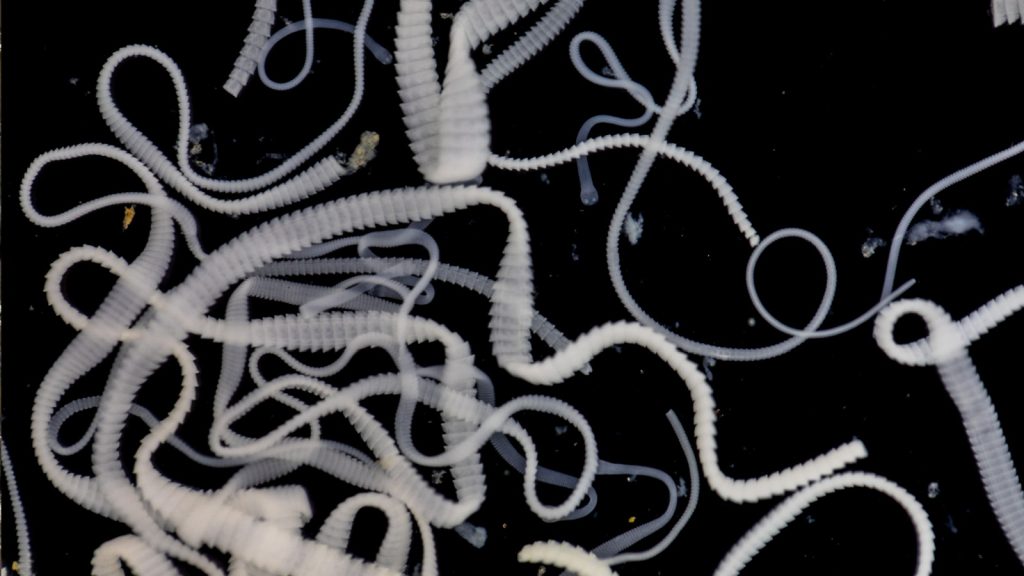

Internal parasites like tapeworms and roundworms can seriously harm wolves’ health. These parasites live in the wolf’s digestive system, stealing nutrients and potentially causing severe illness. Heavy parasite loads can weaken wolves, making them more vulnerable to other threats.
Ticks
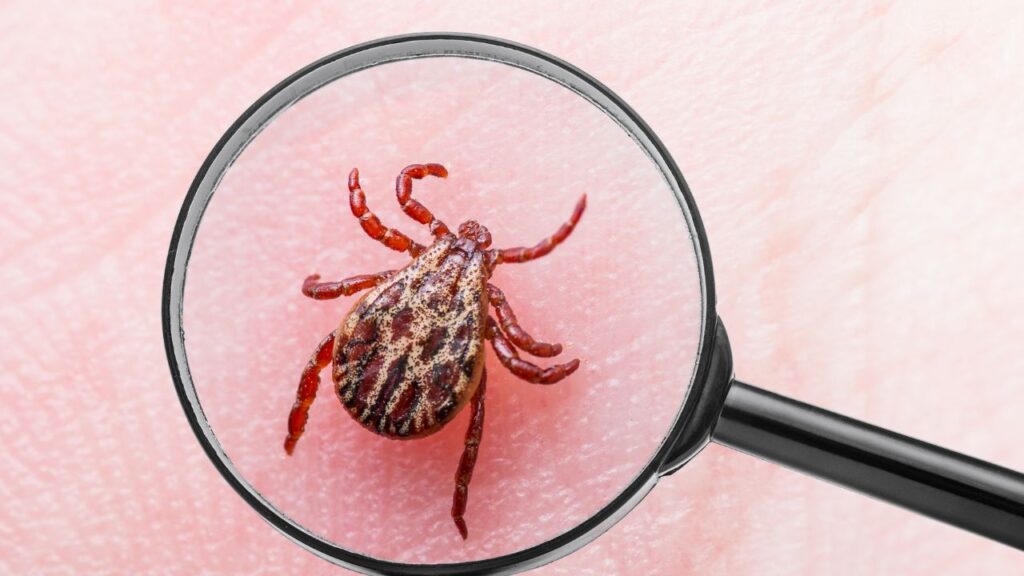

These tiny arachnids are more than just a nuisance for wolves. Ticks can transmit diseases like Lyme disease and Rocky Mountain spotted fever. In large numbers, they can also cause anemia in wolves by draining significant amounts of blood.
Sarcoptic Mange Mites
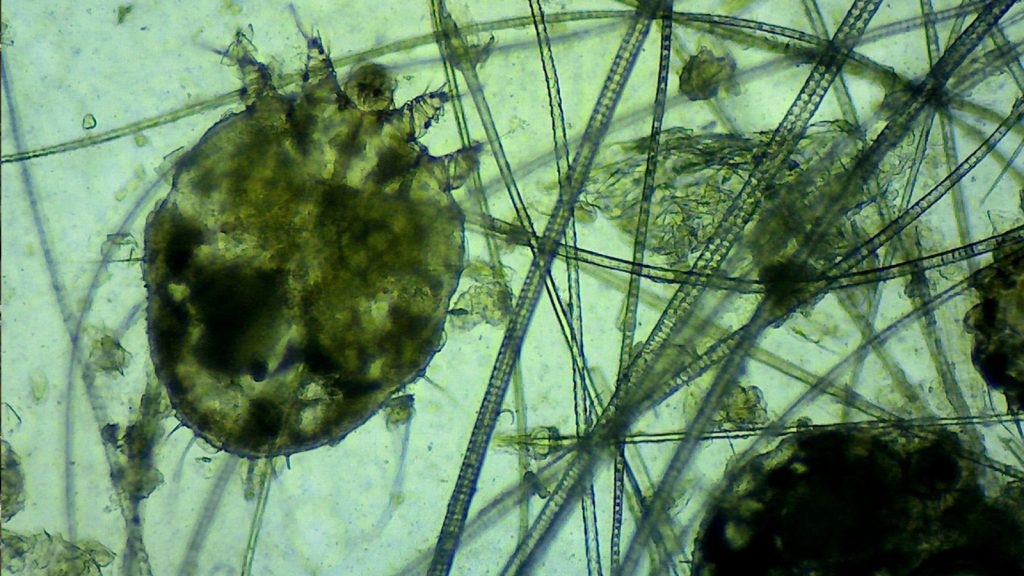
Sarcoptic mange is a skin disease caused by tiny mites. It can be devastating for wolves, causing intense itching, hair loss, and skin infections. Severe cases can lead to death, especially in harsh winter conditions when wolves need their fur for warmth.
Other Wolf Packs
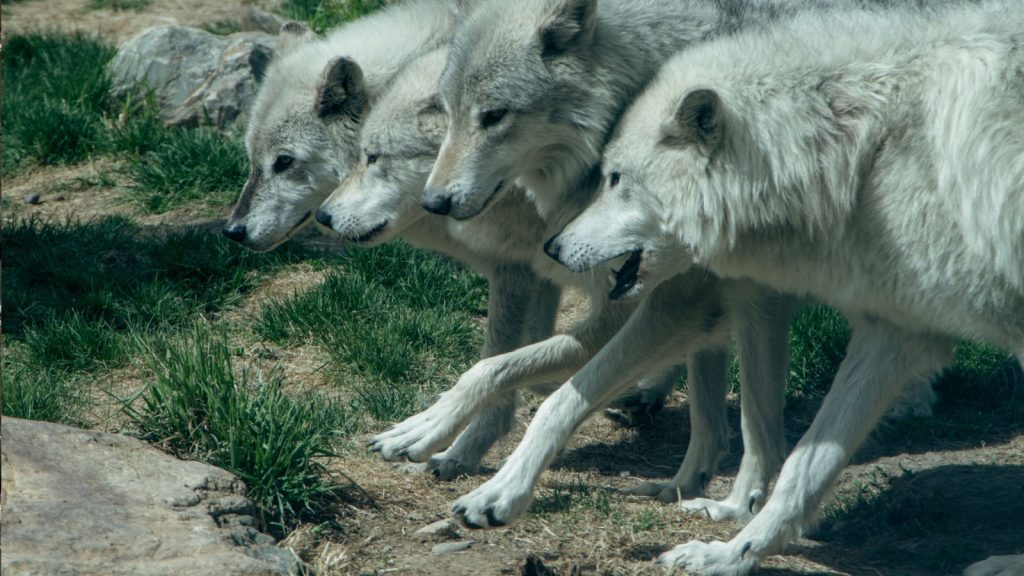

Wolves are territorial animals, and conflicts between packs can be deadly. Rival wolf packs often fight over territory and resources. These battles can result in serious injuries or death for individual wolves.
Golden Eagles
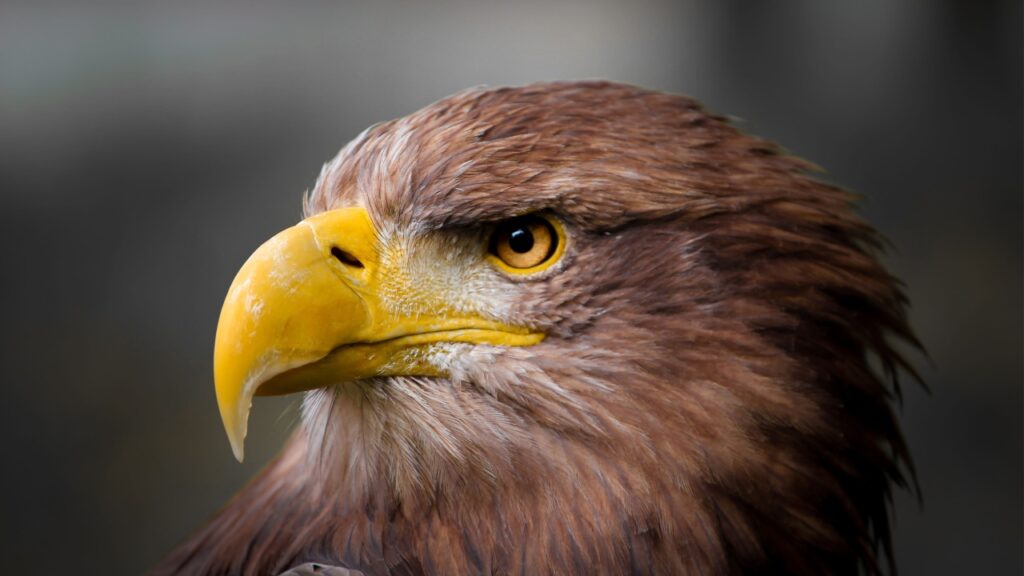

While it might seem surprising, golden eagles have been known to prey on wolf pups. These powerful birds of prey can swoop down and snatch young wolves left unattended. In some areas, eagles pose a significant threat to wolf litter survival.
Alligators
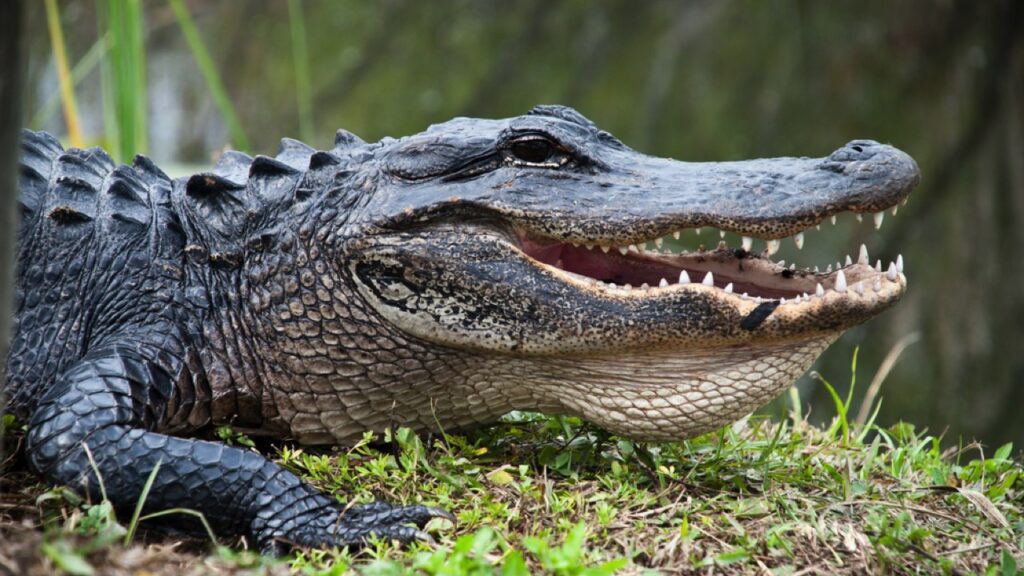

In regions where wolves and alligators coexist, such as parts of the southern United States, alligators can be a threat to wolves. These reptiles might attack wolves that come too close to the water’s edge. Young or sick wolves are particularly vulnerable.
Wolverines
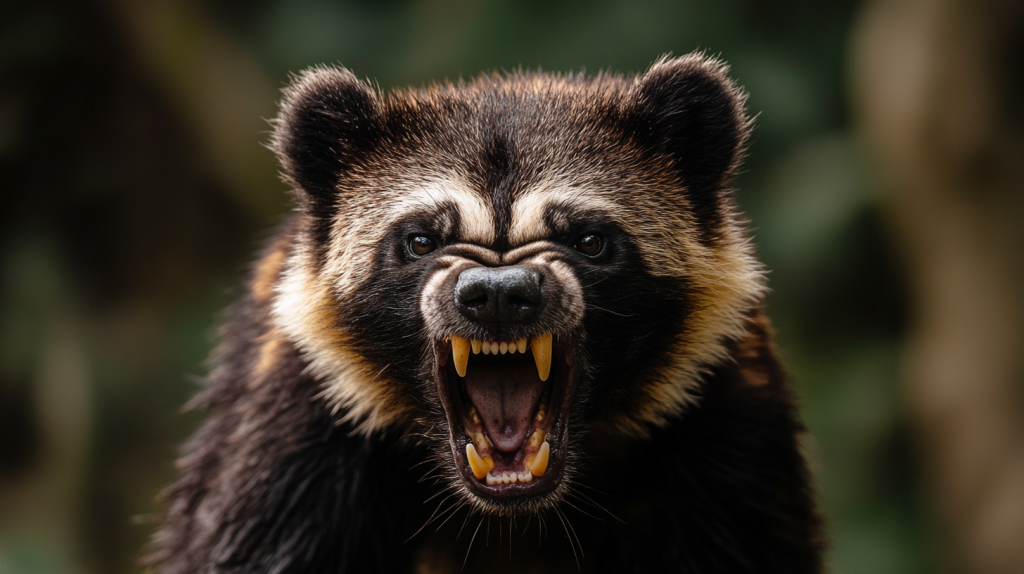

Despite their smaller size, wolverines are fierce predators that can pose a threat to wolves. They’re known for their incredible strength and tenacity. Wolverines might target wolf pups or challenge weak or injured adult wolves.
Coyotes
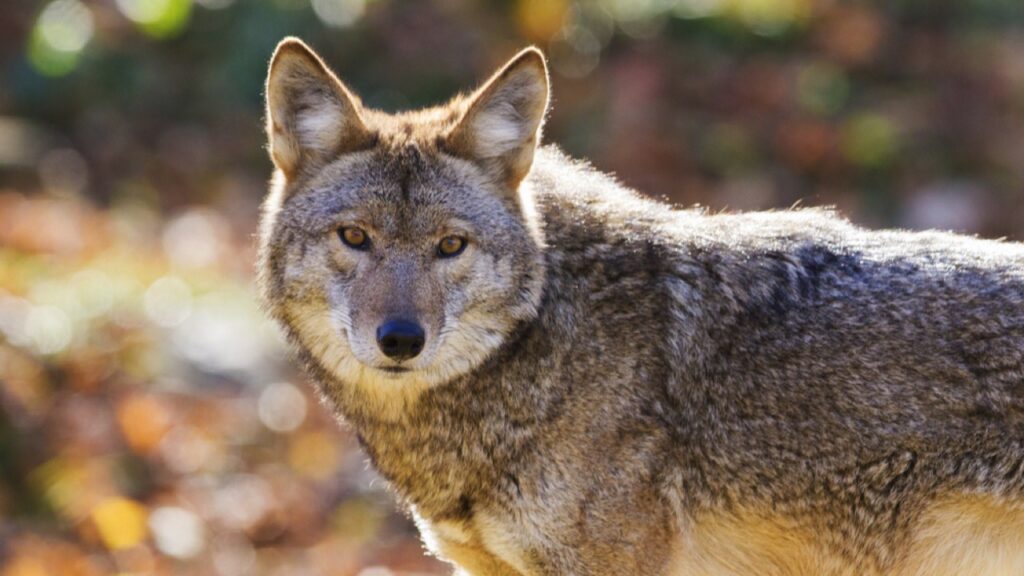

Although wolves are generally dominant over coyotes, large groups of coyotes can pose a threat to lone wolves or pups. In some areas, coyotes compete with wolves for resources and may attack vulnerable wolves opportunistically.



