Nature has a dark side, and parasites are some of its most twisted creations. These creatures have evolved bizarre and often horrifying ways to survive, many of which seem straight out of a horror movie. From mind-controlling fungi to tongue-replacing crustaceans, the world of parasites is full of surprises. Let’s take a look at 14 of the most nightmarish parasites on Earth, each with its own unique and disturbing survival strategy. Prepare yourself for a journey into the weird and wonderful world of nature’s tiniest terrors.
Toxoplasma Gondii

Toxoplasma gondii is a microscopic mastermind that can infect almost any warm-blooded animal, including humans. Its claim to fame? It can alter the behavior of its hosts. Infected rats lose their fear of cats, making them easy prey. In humans, it’s been linked to subtle personality changes and even increased risk-taking behavior.
Cordyceps Fungi
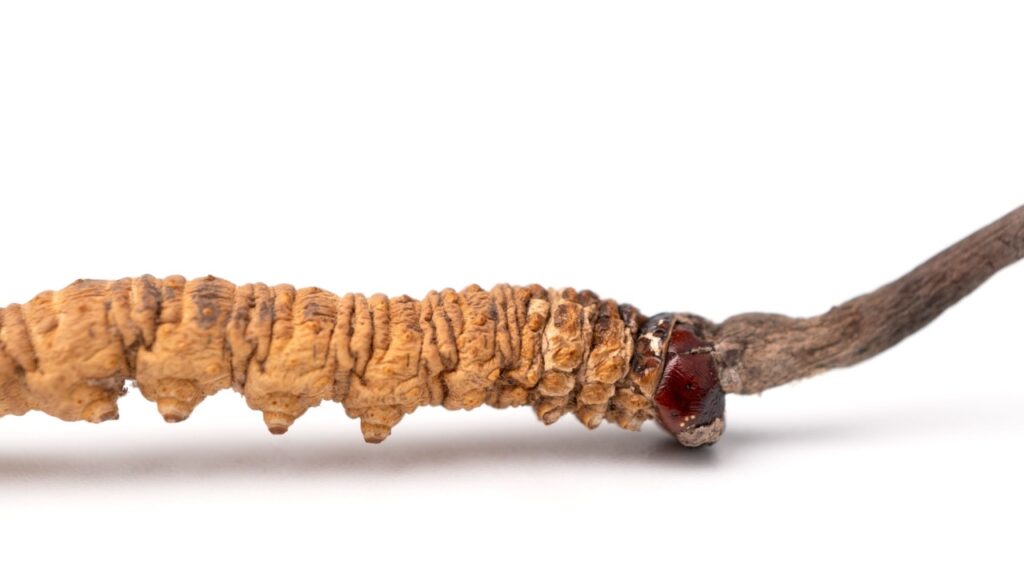

Cordyceps fungi are the stuff of nightmares for insects. These parasites infect their hosts, slowly taking over their bodies and minds. The infected insect, often an ant, is compelled to climb to a high point where the fungus can grow and release its spores. The result is a gruesome “zombie ant” scene straight out of a horror film.
Lancet Liver Fluke

This flatworm has a life cycle that reads like a bizarre adventure novel. It starts in snails, moves to ants, tricks them into climbing grass blades, gets eaten by grazing animals, and finally ends up in their livers. The fluke’s journey showcases nature’s knack for complex, multi-host life cycles.
Hairworm
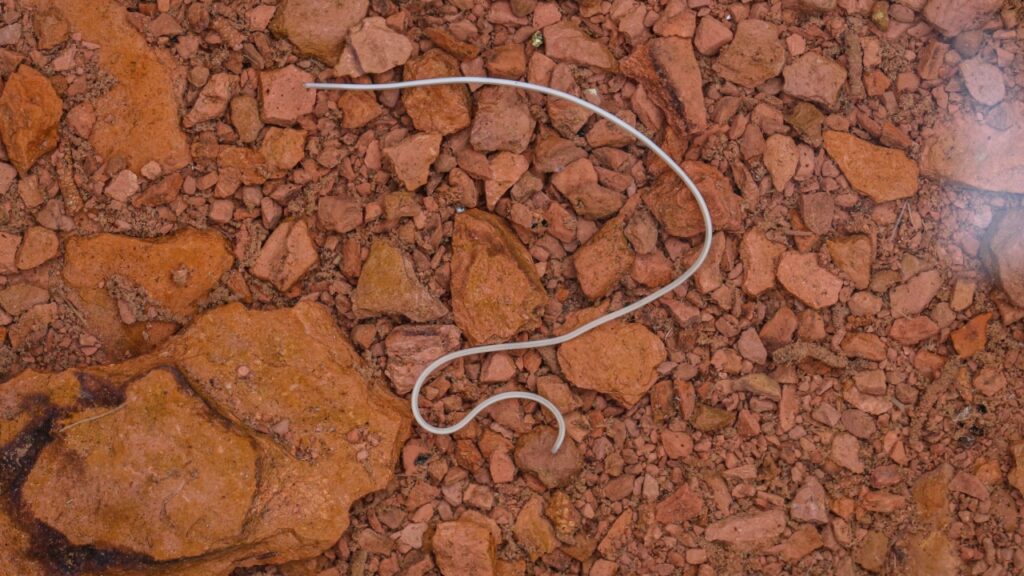

Imagine a worm that can make its host commit suicide. That’s the hairworm’s specialty. It infects insects like grasshoppers and crickets, growing inside them until it’s ready to breed. Then, it manipulates its host to seek out water and jump in, allowing the worm to emerge and find a mate.
Tongue-Eating Louse
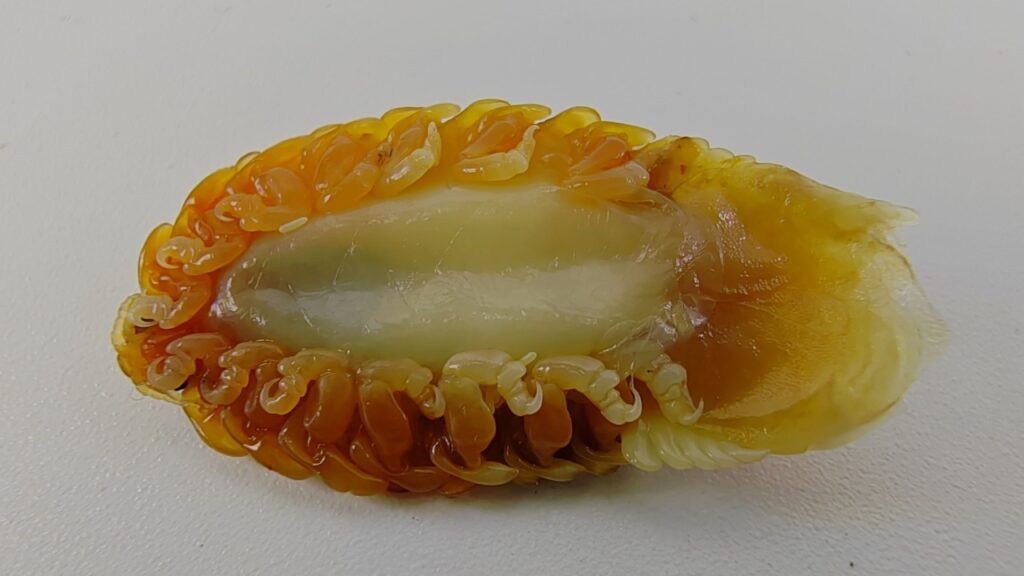

This crustacean is the stuff of dental nightmares. It enters a fish’s body through the gills and latches onto its tongue. Over time, it actually replaces the fish’s tongue, becoming a functional (albeit parasitic) organ. It’s a bizarre example of a parasite becoming an integral part of its host’s anatomy.
Guinea Worm
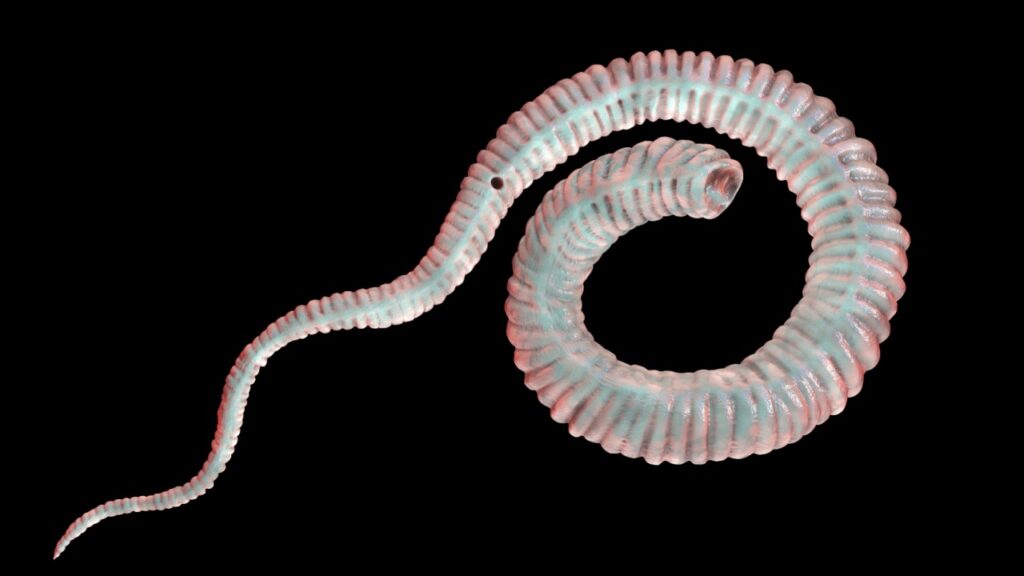
The guinea worm puts its host through a long, painful ordeal. After drinking contaminated water, the host unknowingly ingests the worm’s larvae. A year later, the adult worm emerges through a painful blister, often on the legs or feet. The process of removing the worm can take weeks and is excruciatingly slow.
Botfly
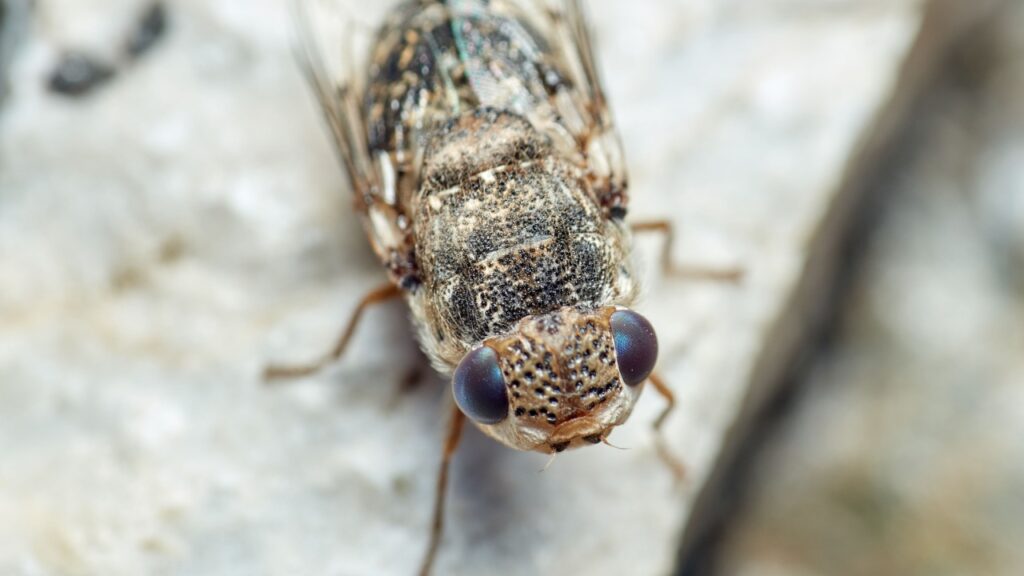

Botflies have a particularly unsettling reproductive strategy. They lay their eggs on mosquitoes, which then transfer the eggs to mammals when they bite. The larvae hatch and burrow into the skin, causing a painful, moving lump. After a few weeks, the mature larva emerges, leaving its unwilling host with a gaping hole.
Echinococcus Tapeworm
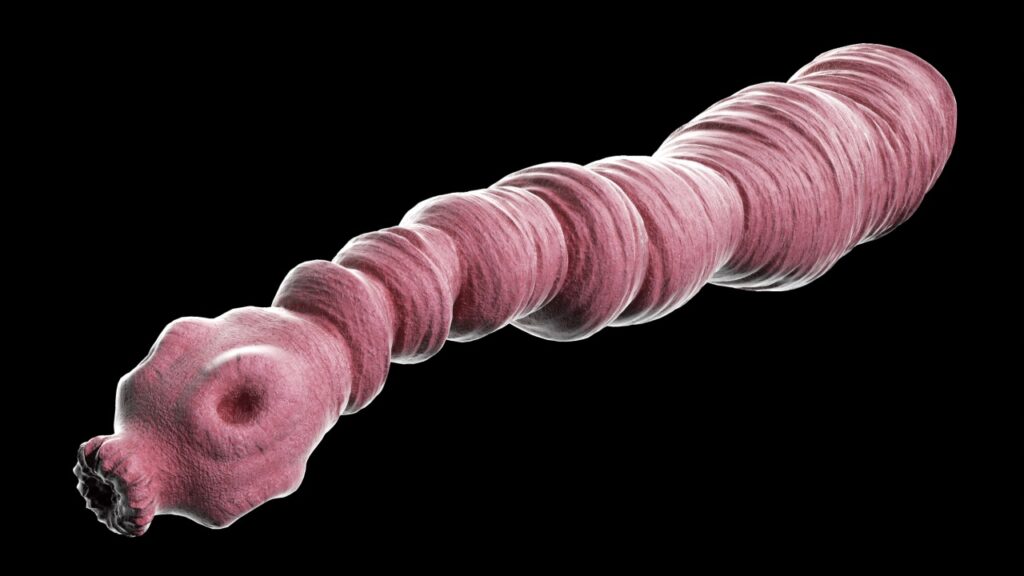
This tiny tapeworm can cause big problems. It typically infects dogs but can spread to humans through contaminated food or water. In humans, it forms cysts in organs like the liver and lungs. These cysts can grow to the size of a softball, causing severe health issues if left untreated.
Parasitic Wasp
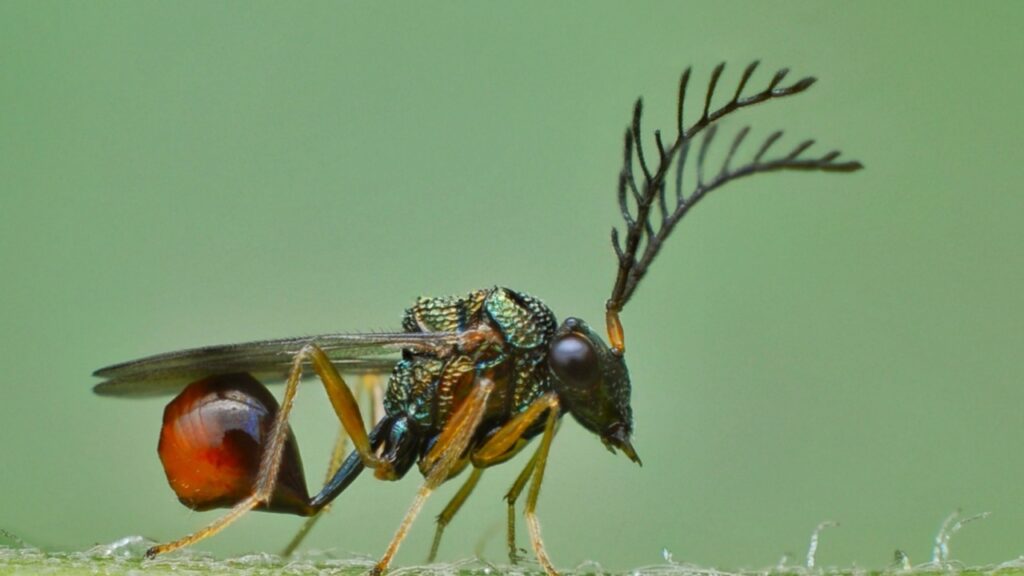

Parasitic wasps are nature’s body snatchers. They lay their eggs inside living hosts, often caterpillars. As the larvae grow, they feed on the host from the inside out. Some species even manipulate the host’s behavior, turning it into a zombie-like guardian for the developing wasps.
Leech
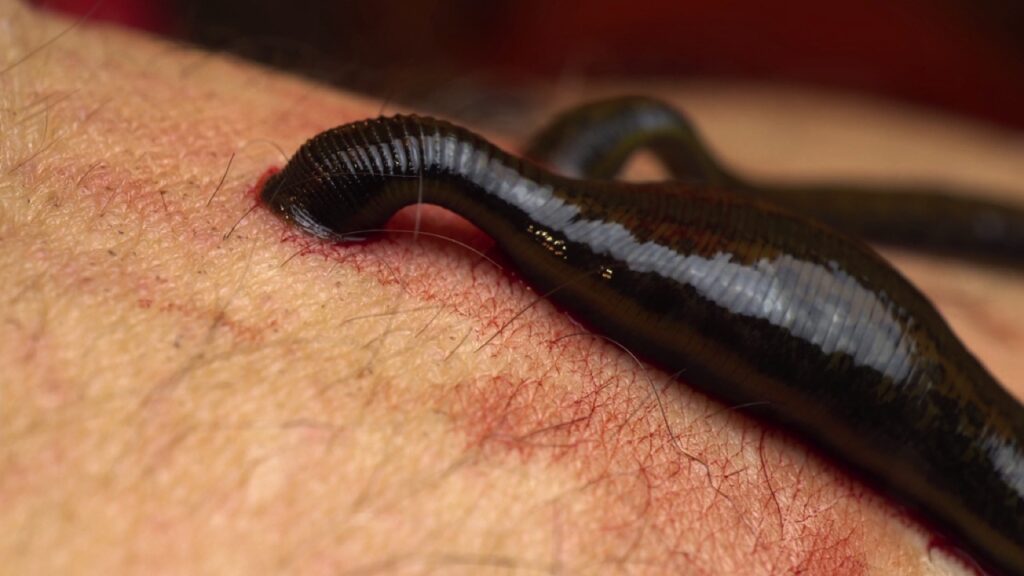

Leeches are the vampires of the parasite world. They attach to their hosts and feed on blood, releasing anticoagulants to keep it flowing. While some species are used in medicine, others can transmit diseases or cause severe anemia in their hosts.
Schistosoma Worm
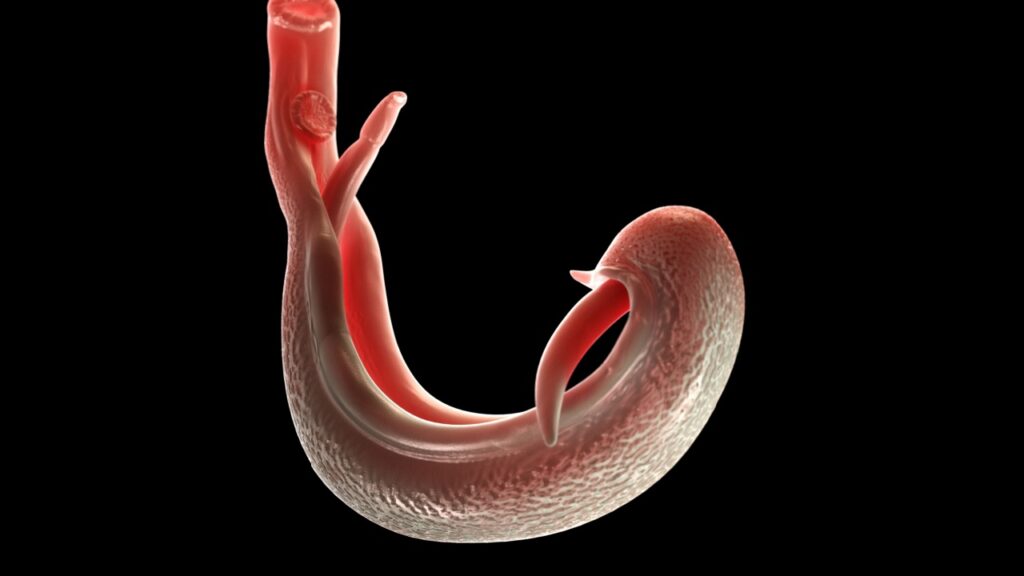
These flatworms cause schistosomiasis, a disease affecting millions worldwide. They lurk in freshwater, penetrating human skin on contact. Once inside, they travel through the bloodstream, potentially damaging various organs. Their eggs can cause inflammation and long-term health problems.
Ascaris Roundworm
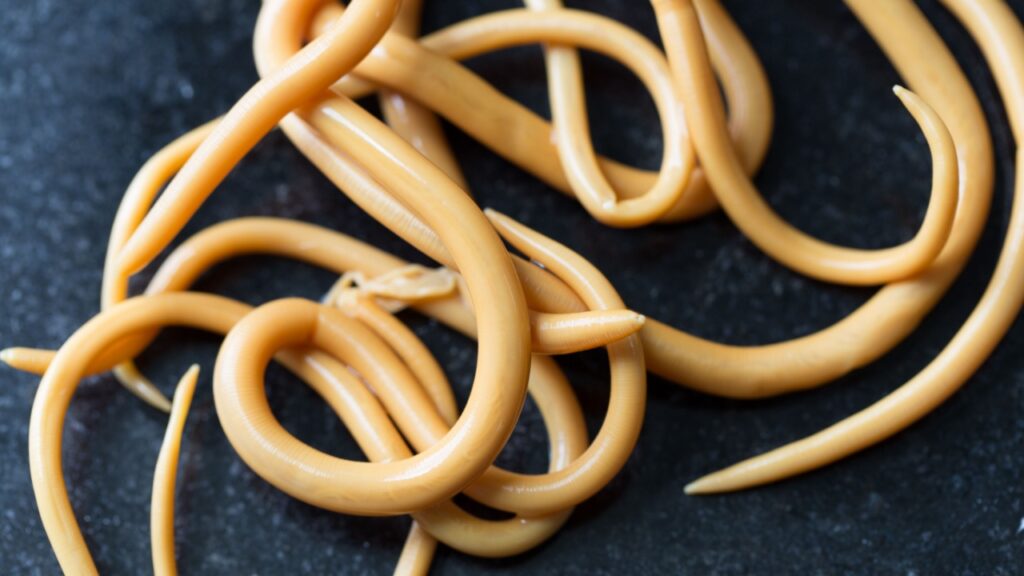

Ascaris roundworms are the giants of intestinal parasites, growing up to a foot long. They infect humans through contaminated soil or food, causing malnutrition and intestinal blockages. A severe infestation can involve hundreds of worms, leading to life-threatening complications.
Rafflesia
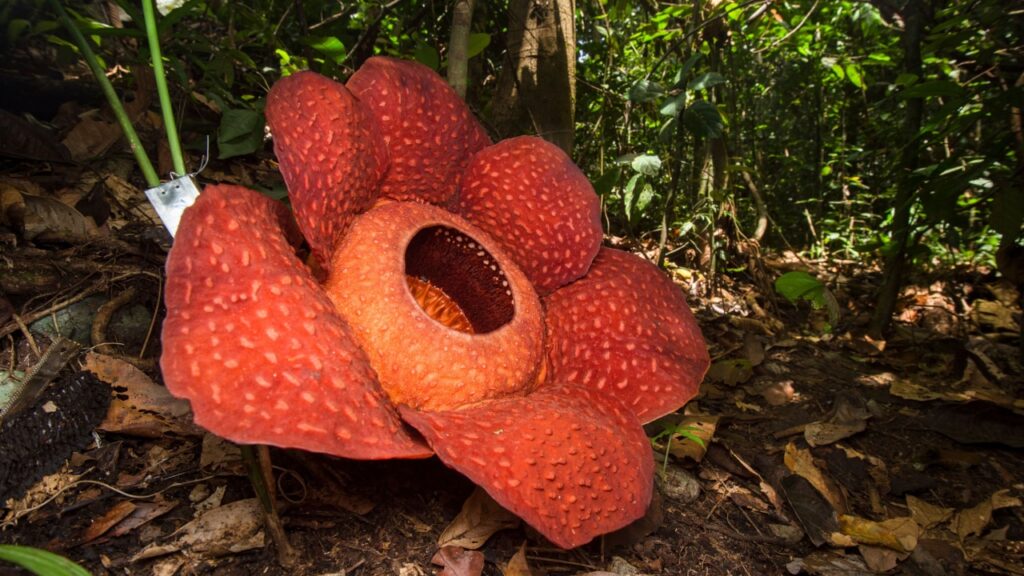

Rafflesia proves that plants can be parasites too. It has no leaves, stems, or roots, relying entirely on its host vine for nutrients. It’s famous for producing the world’s largest flower, which emits a rotting flesh smell to attract pollinators. This bizarre plant challenges our understanding of plant biology and survival strategies.
Leucochloridium paradoxum (The Green-Banded Broodsac)
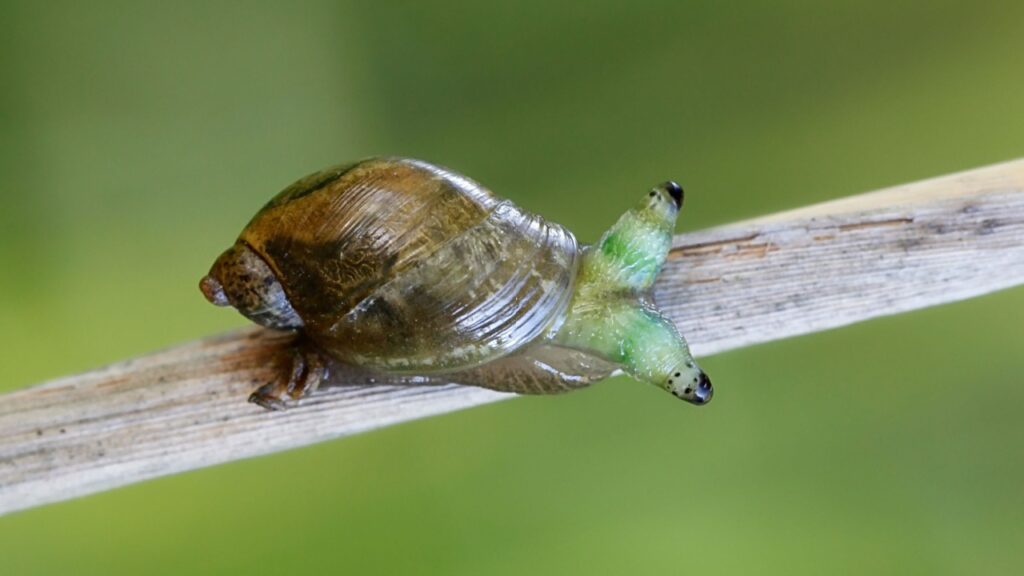

This flatworm parasite has one of the most visually striking strategies in the parasite world. It infects snails and forms pulsating, colorful sacs in their eyestalks. These sacs mimic caterpillars or grubs, attracting birds that eat the infected eyestalks. The parasite then completes its lifecycle in the bird’s digestive system. It’s a remarkable example of a parasite manipulating its host’s appearance to facilitate its own transmission.
Becky is a fervent wildlife enthusiast and pet care expert with a diploma in canine nutrition. Her love for animals stretches beyond the domestic, embracing the wild tapestry of global fauna. With over a decade of experience in animal welfare, Becky lends her expertise to OutlandishOwl through insightful articles, captivating wildlife information, and invaluable guidance on pet nutrition. Her work embodies a deep commitment to understanding the intricate lives of animals and a passion for educating others on sustaining natural habitats. Becky's hands-on conservation efforts and her knack for translating complex dietary science into practical pet feeding tips make her an indispensable voice for creatures great and small.